File:SquareMapConrec6demo.jpg
Original file (711 × 711 pixels, file size: 361 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
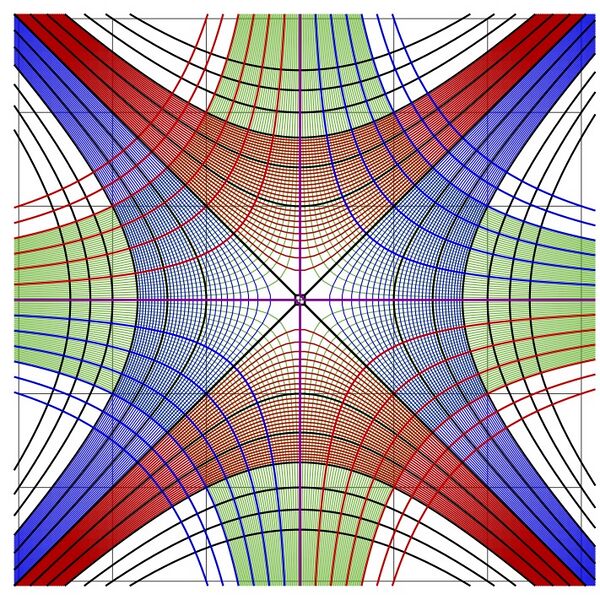
Complex map of Identity function. The map is created for demonstration MapConrec6demo of routine Conrec6.cin.
Routine Conrec6 is created by ChatGPT and Dmitrii Kouznetsov as a modern substitute of historic routine conto.cin from Citizendium [1].
Some features of conto.cin (handling the cut lines) are reproduced in Conrec6.
Some features of conto.cin (handling the saddle points) are not reproduced.
The routine used and the generator are loaded below.
the preliminary version below (used for this picture) may differ from that expected to be loaded later as Conrec6.cin.
Conrec6.cin
// Conrec6.cin
// C++-style include for Conrec6: collects segments, merges into polylines,
// and emits EPS path commands (moveto/lineto) WITHOUT stroking. Caller may set pen before
// and call "S" (stroke) after a group of calls.
// Usage: include this file in your driver (C++), then call Conrec6(...).
// Compilation: The routine does not works with default g++/clang++ as ordinary C++ source including this file.
//For the example below, the following abracadabra is required to compile it:
//c++ -std=c++11 SquareMapConrec6demo.cc -O2 -o SquareMapConrec6demo
#ifndef CONREC_SCALAR_EPS_CIN
#define CONREC_SCALAR_EPS_CIN
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
// Quantization scale used for dedupe/merging; can be adjusted if necessary
static const double CSE_SCALE = 1e8; // quantize to ~1e-8 relative
static inline long long cse_q(double x){ double v = x * CSE_SCALE; return (v>=0.0) ? (long long)(v+0.5) : (long long)(v-0.5); }
struct Seg { double x1,y1,x2,y2; };
static inline int is_finite_d(double x){ return (x==x) && std::isfinite(x); }
// Linear interpolation on edge between (x0,y0) with v0 and (x1,y1) with v1 for level
static inline int interp_xy(double x0,double y0,double v0, double x1,double y1,double v1, double level, double &xo, double &yo){
double denom = (v1 - v0);
if (!is_finite_d(v0) || !is_finite_d(v1) || !is_finite_d(denom)) return 0;
if (std::fabs(denom) < 1e-300){ xo = 0.5*(x0+x1); yo = 0.5*(y0+y1); return 1; }
double t = (level - v0)/denom;
if (t < 0.0) t = 0.0; if (t > 1.0) t = 1.0;
xo = x0 + t*(x1-x0); yo = y0 + t*(y1-y0); return 1;
}
// Helper to emit a polyline without stroking (moveto + many lineto). Caller should set pen and stroke.
static void emit_polyline_nostroke(FILE* out, const std::vector<double>& pts){
if (!out) return;
if (pts.size() < 2) return;
// first point moveto
std::fprintf(out, "%.6g %.6g M ", pts[0], pts[1]);
// subsequent points lineto
for (size_t k=2;k+1<pts.size();k+=2){ std::fprintf(out, "%.6g %.6g L ", pts[k], pts[k+1]); }
std::fprintf(out, "\n");
}
// Key for hashed endpoint: pair of quantized ints packed into string (cheap and portable)
static inline std::string endpoint_key(long long ax, long long ay){ char buf[128]; std::snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"%lld,%lld", ax, ay); return std::string(buf); }
// Main function: collects segments like ms_conrec, merges into polylines, emits moveto/lineto (no stroke)
// field: row-major index = i + j*NX ; X length NX, Y length NY
// Dmax <= 0 disables jump masking (no suppression). Dmax > 0 suppresses edges where |fA-fB| > Dmax
//extern "C" void ConrecScalarEps(FILE* out,
extern "C" void Conrec6(FILE* out,
const double *field,
const double *X,
const double *Y,
int NX,
int NY,
double level,
double Dmax)
{
if (!out || !field || !X || !Y) return;
if (NX < 2 || NY < 2) return;
const double EPS0 = 0.0;
std::vector<Seg> segs;
segs.reserve((NX-1)*(NY-1));
// collect segments
for (int j=0;j<NY-1;++j){
for (int i=0;i<NX-1;++i){
int idx00 = i + j*NX;
int idx10 = i+1 + j*NX;
int idx11 = i+1 + (j+1)*NX;
int idx01 = i + (j+1)*NX;
double f00 = field[idx00]; double f10 = field[idx10]; double f11 = field[idx11]; double f01 = field[idx01];
if (!is_finite_d(f00) || !is_finite_d(f10) || !is_finite_d(f11) || !is_finite_d(f01)) continue;
int b00 = (f00 > level + EPS0) ? 1 : ((f00 < level - EPS0) ? 0 : 2);
int b10 = (f10 > level + EPS0) ? 1 : ((f10 < level - EPS0) ? 0 : 2);
int b11 = (f11 > level + EPS0) ? 1 : ((f11 < level - EPS0) ? 0 : 2);
int b01 = (f01 > level + EPS0) ? 1 : ((f01 < level - EPS0) ? 0 : 2);
if (b00==2 && b10==2 && b11==2 && b01==2) continue;
int s00 = (b00==2)?0:b00; int s10=(b10==2)?0:b10; int s11=(b11==2)?0:b11; int s01=(b01==2)?0:b01;
int mask = (s00?1:0) | (s10?2:0) | (s11?4:0) | (s01?8:0);
if (mask==0 || mask==15) continue;
double x0 = X[i], x1 = X[i+1], y0 = Y[j], y1 = Y[j+1];
double d_bottom = std::fabs(f10 - f00);
double d_right = std::fabs(f11 - f10);
double d_top = std::fabs(f11 - f01);
double d_left = std::fabs(f01 - f00);
bool allow_bottom = (Dmax <= 0.0) || (d_bottom <= Dmax);
bool allow_right = (Dmax <= 0.0) || (d_right <= Dmax);
bool allow_top = (Dmax <= 0.0) || (d_top <= Dmax);
bool allow_left = (Dmax <= 0.0) || (d_left <= Dmax);
double xb,yb,xr,yr,xt,yt,xl,yl;
int has_b=0, has_r=0, has_t=0, has_l=0;
switch (mask){
case 1: case 14:
if (allow_left && allow_bottom){ has_l = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x0,y1,f01, level, xl,yl); has_b = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x1,y0,f10, level, xb,yb); if (has_l && has_b) segs.push_back({xl,yl, xb,yb}); }
break;
case 2: case 13:
if (allow_bottom && allow_right){ has_b = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x1,y0,f10, level, xb,yb); has_r = interp_xy(x1,y0,f10, x1,y1,f11, level, xr,yr); if (has_b && has_r) segs.push_back({xb,yb, xr,yr}); }
break;
case 3: case 12:
if (allow_left && allow_right){ has_l = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x0,y1,f01, level, xl,yl); has_r = interp_xy(x1,y0,f10, x1,y1,f11, level, xr,yr); if (has_l && has_r) segs.push_back({xl,yl, xr,yr}); }
break;
case 4: case 11:
if (allow_right && allow_top){ has_r = interp_xy(x1,y0,f10, x1,y1,f11, level, xr,yr); has_t = interp_xy(x0,y1,f01, x1,y1,f11, level, xt,yt); if (has_r && has_t) segs.push_back({xr,yr, xt,yt}); }
break;
case 5:
if (allow_left && allow_bottom){ has_l = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x0,y1,f01, level, xl,yl); has_b = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x1,y0,f10, level, xb,yb); if (has_l && has_b) segs.push_back({xl,yl, xb,yb}); }
if (allow_right && allow_top){ has_r = interp_xy(x1,y0,f10, x1,y1,f11, level, xr,yr); has_t = interp_xy(x0,y1,f01, x1,y1,f11, level, xt,yt); if (has_r && has_t) segs.push_back({xr,yr, xt,yt}); }
break;
case 6: case 9:
if (allow_bottom && allow_top){ has_b = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x1,y0,f10, level, xb,yb); has_t = interp_xy(x0,y1,f01, x1,y1,f11, level, xt,yt); if (has_b && has_t) segs.push_back({xb,yb, xt,yt}); }
break;
case 7: case 8:
if (allow_left && allow_top){ has_l = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x0,y1,f01, level, xl,yl); has_t = interp_xy(x0,y1,f01, x1,y1,f11, level, xt,yt); if (has_l && has_t) segs.push_back({xl,yl, xt,yt}); }
break;
case 10:
if (allow_bottom && allow_right){ has_b = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x1,y0,f10, level, xb,yb); has_r = interp_xy(x1,y0,f10, x1,y1,f11, level, xr,yr); if (has_b && has_r) segs.push_back({xb,yb, xr,yr}); }
if (allow_left && allow_top){ has_l = interp_xy(x0,y0,f00, x0,y1,f01, level, xl,yl); has_t = interp_xy(x0,y1,f01, x1,y1,f11, level, xt,yt); if (has_l && has_t) segs.push_back({xl,yl, xt,yt}); }
break;
default: break;
}
}
}
if (segs.empty()) return;
// Deduplicate segments by quantized endpoints (canonicalize end order)
std::vector<Seg> good; good.reserve(segs.size());
std::unordered_map<std::string, int> seen; seen.reserve(segs.size()*2);
for (size_t s=0;s<segs.size();++s){
double ax = segs[s].x1, ay = segs[s].y1, bx = segs[s].x2, by = segs[s].y2;
// canonical order
if (ax > bx || (ax==bx && ay>by)){ std::swap(ax,bx); std::swap(ay,by); }
long long a_x = cse_q(ax), a_y = cse_q(ay), b_x = cse_q(bx), b_y = cse_q(by);
std::string key = endpoint_key(a_x,a_y) + "|" + endpoint_key(b_x,b_y);
if (seen.find(key) == seen.end()){ seen[key] = 1; good.push_back({ax,ay,bx,by}); }
}
segs.swap(good);
if (segs.empty()) return;
// Build adjacency: map key -> vector of segment indices
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<int> > adj;
adj.reserve(segs.size()*2);
auto add_adj = [&](long long qx, long long qy, int idx){ std::string k = endpoint_key(qx,qy); adj[k].push_back(idx); };
for (int i=0;i<(int)segs.size();++i){
long long a_x = cse_q(segs[i].x1), a_y = cse_q(segs[i].y1);
long long b_x = cse_q(segs[i].x2), b_y = cse_q(segs[i].y2);
add_adj(a_x,a_y,i); add_adj(b_x,b_y,i);
}
// Find endpoints with degree 1 to start polylines
std::vector<int> used(segs.size(),0);
std::vector< std::vector<double> > polylines; polylines.reserve(segs.size()/2 + 4);
// helper to follow chain from endpoint
auto follow_chain = [&](long long start_x, long long start_y){
std::string sk = endpoint_key(start_x,start_y);
std::vector<double> pts; pts.reserve(64);
// find a segment touching start
auto it = adj.find(sk);
if (it==adj.end()) return pts;
int segidx = -1;
for (int si : it->second) if (!used[si]) { segidx = si; break; }
if (segidx<0) return pts;
// determine orientation so that segidx starts at this endpoint
double cx, cy; cx = (double)start_x / CSE_SCALE; cy = (double)start_y / CSE_SCALE; // approximate; will replace real coords below
// We'll trace forward
int cur = segidx; int prev_end = 0; // 0 means unknown
while (cur >= 0){
if (used[cur]) break;
used[cur] = 1;
// get seg endpoints as precise doubles
double ax = segs[cur].x1, ay = segs[cur].y1, bx = segs[cur].x2, by = segs[cur].y2;
// if pts empty, push ax,ay,bx,by in orientation matching start
if (pts.empty()){
// check which endpoint matches start (by quantized equality)
long long qa_x = cse_q(ax), qa_y = cse_q(ay), qb_x = cse_q(bx), qb_y = cse_q(by);
if (qa_x==start_x && qa_y==start_y){ pts.push_back(ax); pts.push_back(ay); pts.push_back(bx); pts.push_back(by); prev_end = qb_x==qa_x && qb_y==qa_y ? 0 : 1; }
else { pts.push_back(bx); pts.push_back(by); pts.push_back(ax); pts.push_back(ay); prev_end = 1; }
} else {
// append the far endpoint only
double lastx = pts[pts.size()-2], lasty = pts[pts.size()-1];
// find which endpoint of segment matches last point (quantized)
long long q_lastx = cse_q(lastx), q_lasty = cse_q(lasty);
long long qa_x = cse_q(ax), qa_y = cse_q(ay), qb_x = cse_q(bx), qb_y = cse_q(by);
if (qa_x==q_lastx && qa_y==q_lasty){ pts.push_back(bx); pts.push_back(by); prev_end = 1; }
else if (qb_x==q_lastx && qb_y==q_lasty){ pts.push_back(ax); pts.push_back(ay); prev_end = 1; }
else { /* not connected - stop */ break; }
}
// find next segment that shares the new endpoint (last point)
double newx = pts[pts.size()-2], newy = pts[pts.size()-1];
long long nq_x = cse_q(newx), nq_y = cse_q(newy);
std::string nk = endpoint_key(nq_x,nq_y);
int next_seg = -1;
auto it2 = adj.find(nk);
if (it2!=adj.end()){
for (int cand : it2->second) if (!used[cand]) { next_seg = cand; break; }
}
cur = next_seg;
}
return pts;
};
// start from degree-1 nodes
for (auto &kv : adj){ if ((int)kv.second.size() == 1){ // endpoint
// extract quantized coords from key string
const std::string &k = kv.first; long long qx=0,qy=0; if (std::sscanf(k.c_str(), "%lld,%lld", &qx, &qy)==2){
std::vector<double> poly = follow_chain(qx,qy);
if (poly.size() >= 4) polylines.push_back(poly);
}
}}
// remaining segments -> cycles
for (int si=0; si<(int)segs.size(); ++si){ if (!used[si]){
// pick one endpoint of seg si as start
long long qa_x = cse_q(segs[si].x1), qa_y = cse_q(segs[si].y1);
std::vector<double> poly = follow_chain(qa_x, qa_y);
if (poly.size() >= 4) polylines.push_back(poly);
}}
// Optional: simplify polylines by merging nearly-collinear triplets
auto simplify_poly = [](std::vector<double>& pts){
if (pts.size() < 6) return;
std::vector<double> out; out.reserve(pts.size());
out.push_back(pts[0]); out.push_back(pts[1]);
for (size_t k=2;k+1<pts.size();k+=2){
double x0 = out[out.size()-2], y0 = out[out.size()-1];
double x1 = pts[k], y1 = pts[k+1];
double x2 = (k+2<pts.size())? pts[k+2] : NAN; double y2 = (k+2<pts.size())? pts[k+3] : NAN;
if (k+2 < pts.size()){
// check collinearity of (x0,y0)-(x1,y1)-(x2,y2)
double ux = x1-x0, uy = y1-y0;
double vx = x2-x1, vy = y2-y1;
double cross = ux*vy - uy*vx;
double norm = std::sqrt((ux*ux+uy*uy)*(vx*vx+vy*vy));
if (norm > 0 && std::fabs(cross)/norm < 1e-9){ // nearly collinear -> skip current middle point
// do nothing (skip adding x1,y1)
continue;
}
}
out.push_back(x1); out.push_back(y1);
}
pts.swap(out);
};
for (auto &pl : polylines){ simplify_poly(pl); emit_polyline_nostroke(out, pl); }
}
#endif // CONREC_SCALAR_EPS_CIN
SquareMapConrec6demo.cc
// Files conto.cin and the "Conrec6.cin" above should be loaded in order to compile the generator below.
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <complex>
using std::complex;
typedef double DB;
typedef complex<double> z_type;
#include "ado.cin"
#include "Conrec6.cin" /* the scalar tracer above */
int main(){ const int NX = 63, NY = 62; /* points; cells are 120x120 */
double *X = (double*)malloc(NX*sizeof(double));
double *Y = (double*)malloc(NY*sizeof(double));
double *R = (double*)malloc(NX*NY*sizeof(double));
double *I = (double*)malloc(NX*NY*sizeof(double));
for (int i=0;i<NX;++i) X[i] = -3 + .1*(i-.5);
for (int j=0;j<NY;++j) Y[j] = -3 + .1*(j-.5);
for (int j=0;j<NY;++j){
for (int i=0;i<NX;++i){ z_type z(X[i], Y[j]); z_type f;
f=z*z;
R[i + j*NX] = f.real();
I[i + j*NX] = f.imag();
}}
FILE* o = fopen("SquareMapConrec6demo.eps","w"); ado(o, 640, 640); fprintf(o, "320 320 translate\n 100 100 scale\n");
for (int k=-3;k<=3;++k){
fprintf(o,"%d -3 M %d 3 L 0 0 0 RGB .006 W S\n", k, k);
fprintf(o,"-3 %d M 3 %d L 0 0 0 RGB .006 W S\n", k, k);
}
//const double DMAX = 2.; /* set >0 to enable jump masking, e.g. 2.5 for log */
const double DMAX = 4.; /* set >0 to enable jump masking, e.g. 2.5 for log */
for(int n=-4; n<4; n++)
for(int m=1; m<10; m++) Conrec6(o, I, X,Y,NX,NY, n+.1*m, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0.7 0 RGB .01 W S\n");
for(int n=0; n<3; n++)
for(int m=1; m<10; m++) Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY,-(n+.1*m), DMAX); fprintf(o,".8 0 0 RGB .014 W S\n");
for(int n=0; n<3; n++)
for(int m=1; m<10; m++) Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY, n+.1*m, DMAX); fprintf(o,".0 0 .9 RGB .01 W S\n");
for(int m=1;m<7; m++) Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY, -m, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0 0 RGB .02 W S\n");
for(int m=1;m<7; m++) Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY, m, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0 0 RGB .02 W S\n");
for(int m=1; m<7; m++) Conrec6(o, I, X,Y,NX,NY,-m, DMAX); fprintf(o,".9 0 0 RGB .02 W S\n");
for(int m=1; m<7; m++) Conrec6(o, I, X,Y,NX,NY, m, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0 .9 RGB .02 W S\n");
Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY, -1.e-8, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0 0 RGB .024 W S\n");
Conrec6(o, R, X,Y,NX,NY, 1.e-8, DMAX); fprintf(o,"0 0 0 RGB .024 W S\n");
Conrec6(o, I, X,Y,NX,NY, -1.e-8, DMAX); fprintf(o,".6 0 .6 RGB .024 W S\n");
Conrec6(o, I, X,Y,NX,NY, 1.e-8, DMAX); fprintf(o,".6 0 .6 RGB .024 W S\n");
fprintf(o,"showpage\n"); fclose(o);
system("epstopdf SquareMapConrec6demo.eps");
system( "open SquareMapConrec6demo.pdf"); //for macintosh
//system( "xpdf SquareMapConrec6demo.pdf"); //for Linux
free(X); free(Y); free(R); free(I);
return 0;
}
References
- ↑ https://en.citizendium.org/wiki/Contour_plot/Code/conto.cin // Copyleft 2008 by Dmitrii Kouznetsov This page was last modified 01:05, 2 February 2009.
Keywords
«Ado.cin», «ChatGPT», «Complex map», «conto.cin», «MapConrec6demo», «Power function»,
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:32, 5 September 2025 |  | 711 × 711 (361 KB) | T (talk | contribs) | == Summary == {{oq|SquareMapConrec6demo.jpg|Original file (711 × 711 pixels, file size: 361 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg) }} Complex map of Identity function. The map is created for demonstration MapConrec6demo of routine Conrec6.cin. Routine Conrec6 is created by ChatGPT and Dmitrii Kouznetsov as a modern substitute of historic routine conto.cin from Citizendium <ref> https://en.citizendium.org/wiki/Contour_plot/Code/conto.cin // Copyleft 2008 by Dmitrii Kouzn... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: