BesselH0
BesselH0\((z)=H_0(z)\!=\)HankelH1\([0,z]\) is the Cylindric function H (called also the Hankel function) of zero order.
BesselH0 is related with \(J_0=\)BesselJ0 and \(J_0=\)BesselY0 with simple relation
- \(H_0(z)=J_0(z)+\mathrm i Y_0(z)\)
In particular, for \(x>0\), the relations \(\Im(J_0(x))=0\) and \(\Im(Y_0(x))=0\) hold, and, therefore,
- \(\Re(H_0(x))=J_0(x)\)
- \(\Im(H_0(x))=Y_0(x)\)
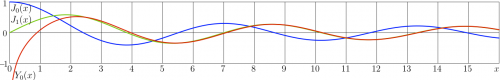
The explicit plot of real and imaginary parts of BesselH0 versus real positive argument are shown in the upper right corner.
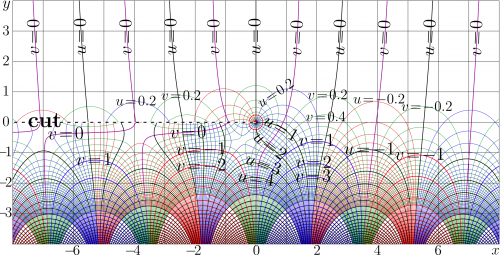
Below, the complex map of \(H_0\) is plotted, \(u+\mathrm i v=H_0(x+\mathrm i y)\).
Asymptotic expansions
TeXForm[Expand[Series[(HankelH1[0, x]) (Pi I x/2)^(1/2), {x, Infinity, 5}]]]
does
\(e^{i x} \left(1-\frac{i}{8 x}-\frac{9}{128 x^2}+\frac{75 i}{1024 x^3}+\frac{3675}{32768 x^4}-\frac{59535 i}{262144 x^5}+O\left(\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^6\right)\right)\)
Square of BesselH0
Some expansions of square of BesselH0 look counter-intuitive and require analysis. One example ix copy pasted below.
TeXForm[Expand[Series[(HankelH1[0, x])^2 Pi I x/2, {x, Infinity, 5}]]]
does
\(e^{2 i x} \left(1-\frac{i}{4 x}-\frac{5}{32 x^2}+\frac{21 i}{128 x^3}+\frac{507}{2048 x^4}-\frac{4035 i}{8192 x^5}+O\left(\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^6\right)\right)\)
and
TeXForm[Expand[Series[(HankelH1[0, x^(1/2)])^2 Pi I x^(1/2)/2, {x, Infinity, 2}]]]
does
\(e^{2 i \sqrt{x}} \left(1-\frac{1}{4} i \sqrt{\frac{1}{x}}-\frac{5}{32 x}+\frac{21}{128} i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{3/2}+\frac{381}{16384 x^2}-\frac{675 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{5/2}}{65536}+O\left(\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^3\right)\right) \)
At least one of these two asymptotic expansions seems to be wrong. Perhaps, the last one, because
TeXForm[Expand[Series[(HankelH1[0, x^(1/2)])^2 Pi I x^(1/2)/2, {x, Infinity, 3}]]]
does
\(e^{2 i \sqrt{x}} \left(1-\frac{1}{4} i \sqrt{\frac{1}{x}}-\frac{5}{32 x}+\frac{21}{128} i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{3/2}+\frac{507}{2048 x^2}-\frac{5025 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{5/2}}{131072}-\frac{44325}{2 097152 x^3}+\frac{275625 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{7/2}}{16777216}+O\left(\left (\frac{1}{x}\right)^4\right)\right)\)
Correcting the two terms (that showes deviation in the previous example); however, two new wrong terms are added. The control on the precision seems to be lost, because
TeXForm[Expand[Series[(HankelH1[0, x^(1/2)])^2 Pi I x^(1/2)/2, {x, Infinity, 4}]]]
does
\(e^{2 i \sqrt{x}} \left(1-\frac{1}{4} i \sqrt{\frac{1}{x}}-\frac{5}{32 x}+\frac{21}{128} i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{3/2}+\frac{507}{2048 x^2}-\frac{4035 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{5/2}}{8192}-\frac{163395}{20 97152 x^3}+\frac{50715 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{7/2}}{1048576}+\frac{4922662 5}{1073741824 x^4}-\frac{218791125 i \left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{9/2}}{4294967296}+O\left(\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^5\right)\right)\)
This phenomenon can be interpreted as bug in Mathematica Series routine.