Difference between revisions of "NemBra"
m (Text replacement - "\$([^\$]+)\$" to "\\(\1\\)") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Nembraplot.jpg|100px|thumb| |
+ | [[File:Nembraplot.jpg|100px|thumb|\(x\!+\!\mathrm i y\!=\!\mathrm{Nembra}(q)\) for real \(q\)]] |
[[NemBra]] is holomorphic function that expresses values of the [[Nemtsov function]] |
[[NemBra]] is holomorphic function that expresses values of the [[Nemtsov function]] |
||
at its brach point, as function of the parameter of the Nemtsov function. |
at its brach point, as function of the parameter of the Nemtsov function. |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The [[Nemtsov function]] is polynomial of 4th order of special kind, |
The [[Nemtsov function]] is polynomial of 4th order of special kind, |
||
| − | + | \(\mathrm{Nem}_q(z)=z+z^3+qz^4\) |
|
its derivative |
its derivative |
||
| − | + | \(\mathrm{Nem}_q'(z)=1+3z^2+4qz^3\) |
|
| − | If |
+ | If \(z=\mathrm{NemBra}(q)~\) , then \(\mathrm{Nem}_q'(z)=0\) |
| − | The inverse function of the Nemtsov function, id est, |
+ | The inverse function of the Nemtsov function, id est, \(\mathrm{ArcNem}_q=\mathrm{Nem}_q^{-1}\) |
| − | has branchpoint |
+ | has branchpoint \(\mathrm{Nem}_q(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\) |
For real values of the argument, the [[parametric plot]] of function [[NemBra]] is shown in figure at right: line |
For real values of the argument, the [[parametric plot]] of function [[NemBra]] is shown in figure at right: line |
||
| − | + | \(x=\Re(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\), |
|
| − | + | \(y=\Im(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\) |
|
| − | is drawn in the |
+ | is drawn in the \(x\), \(y\) plane. Corresponding values of \(q\) are marked along the curve. |
==Special case: value at zero== |
==Special case: value at zero== |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
There is specific value at zero: |
There is specific value at zero: |
||
| − | + | \(z_0=\mathrm{NemBra}(0)=\mathrm i /\sqrt{3} \approx 0.6\, \mathrm i\) |
|
Then, function [[NemBran]] at zero can be expressed: |
Then, function [[NemBran]] at zero can be expressed: |
||
| − | + | \(~ \displaystyle |
|
\mathrm{Nembran}(0) = \mathrm{Nembra}(z_0) = |
\mathrm{Nembran}(0) = \mathrm{Nembra}(z_0) = |
||
\frac{\mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3\, \mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}} = |
\frac{\mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3\, \mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}} = |
||
| − | \sqrt{\frac{4}{27}}\, \mathrm i \approx 0.4\, \mathrm i |
+ | \sqrt{\frac{4}{27}}\, \mathrm i \approx 0.4\, \mathrm i\) |
==Explicit representation and the evaluation== |
==Explicit representation and the evaluation== |
||
| − | At given |
+ | At given \(q\), the cubic equation |
| − | + | \(1+3z^2+4qz^3 = 0\) |
|
| − | has 3 solutions. For positive |
+ | has 3 solutions. For positive \(q\), one of these solutions is real and negative, and does not bring new the cut lines of finction [[ArqNem]], as anyway it has cut along the negative part of the real axis. Two other solutions are related with complex conjugation; so, for the evaluation, it is sufficient co consider one of them. |
| − | Namely this solution is denoted with name [[NemBra]] and shown in the parametric plot at right hand side figure as function of |
+ | Namely this solution is denoted with name [[NemBra]] and shown in the parametric plot at right hand side figure as function of \(q\). |
Function NemBra can be represented explicitly with combination of radicals, at the appropriate choice of the branch of these radicals. |
Function NemBra can be represented explicitly with combination of radicals, at the appropriate choice of the branch of these radicals. |
||
| − | Let |
+ | Let \(~ \rho=-1-8q^2+4\sqrt{q^2+4q^4}\) |
| − | Let |
+ | Let \(~ V=\rho^{1/3}\) |
| − | Then |
+ | Then \(~ \displaystyle |
| − | \mathrm{NemBra}(q)=\frac{1}{4q}\left(-1+V+1/V\right) |
+ | \mathrm{NemBra}(q)=\frac{1}{4q}\left(-1+V+1/V\right)\) |
| − | Extension of power |
+ | Extension of power \(1/3\) beyond the cut line and the same about the square root above provides other solutions |
and other branch points of function [[ArqNem]]. |
and other branch points of function [[ArqNem]]. |
||
==Inverse function== |
==Inverse function== |
||
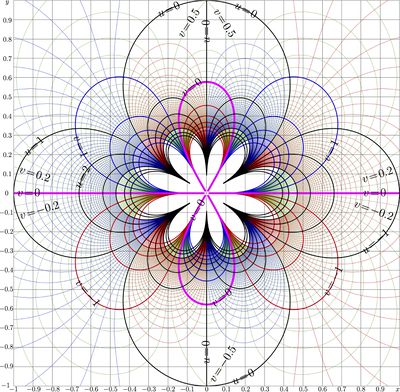
| − | [[File:Arcnembrat.jpg|400px|thumb| |
+ | [[File:Arcnembrat.jpg|400px|thumb| \(u\!+\!\mathrm i v=\mathrm{ArcNemBra}(x\!+\!\mathrm i y)\)]] |
Inverse function of NemBra is denoted with [[ArcNemBra]]. In such a way, |
Inverse function of NemBra is denoted with [[ArcNemBra]]. In such a way, |
||
| − | + | \(\mathrm{NemBra}(\mathrm{ArcNemBra}(z))=z\) |
|
ArcNemBra is [[elementary function]], |
ArcNemBra is [[elementary function]], |
||
| − | + | \(\displaystyle |
|
| − | \mathrm{ArcNemBra}(z)= - \frac{1\!+\! 3z^2}{4\, z^3} |
+ | \mathrm{ArcNemBra}(z)= - \frac{1\!+\! 3z^2}{4\, z^3}\) |
| − | Complex map of function [[ArcNemBra]] is shown in figure at right; |
+ | Complex map of function [[ArcNemBra]] is shown in figure at right; \(u\!+\!\mathrm i v=\mathrm{ArcNemBra}(x\!+\!\mathrm i y\). |
| − | Lines |
+ | Lines \(u\!=\!\mathrm{const}\) and |
| − | lines |
+ | lines \(u\!=\!\mathrm{const}\) are drawn in the \(x\), \(y\) plane. |
| − | Level |
+ | Level \(v\!=\!0\) iz marked with pink line. In the First quadrant of the \(x\), \(y\) plane, It is the same line, as the [[parametric plot]] of function [[NemBra]] for real values of the argument. |
==Usage== |
==Usage== |
||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
Function [[ArqNem]] is inverse function of the [[Nemtsov function]]; |
Function [[ArqNem]] is inverse function of the [[Nemtsov function]]; |
||
| − | + | \(\mathrm{Nem}_q(\mathrm{ArqNem}_q(z))=z\) |
|
Function [[ArqNem]] is necessary for evaluation of iterates of the [[Nemtsov function]], constructed at zero. |
Function [[ArqNem]] is necessary for evaluation of iterates of the [[Nemtsov function]], constructed at zero. |
||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 30 July 2019
NemBra is holomorphic function that expresses values of the Nemtsov function at its brach point, as function of the parameter of the Nemtsov function.
Description
The Nemtsov function is polynomial of 4th order of special kind,
\(\mathrm{Nem}_q(z)=z+z^3+qz^4\)
its derivative
\(\mathrm{Nem}_q'(z)=1+3z^2+4qz^3\)
If \(z=\mathrm{NemBra}(q)~\) , then \(\mathrm{Nem}_q'(z)=0\)
The inverse function of the Nemtsov function, id est, \(\mathrm{ArcNem}_q=\mathrm{Nem}_q^{-1}\)
has branchpoint \(\mathrm{Nem}_q(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\)
For real values of the argument, the parametric plot of function NemBra is shown in figure at right: line
\(x=\Re(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\),
\(y=\Im(\mathrm{NemBra}(q))\)
is drawn in the \(x\), \(y\) plane. Corresponding values of \(q\) are marked along the curve.
Special case: value at zero
There is specific value at zero:
\(z_0=\mathrm{NemBra}(0)=\mathrm i /\sqrt{3} \approx 0.6\, \mathrm i\)
Then, function NemBran at zero can be expressed:
\(~ \displaystyle \mathrm{Nembran}(0) = \mathrm{Nembra}(z_0) = \frac{\mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}}-\frac{3\, \mathrm i}{\sqrt{3}} = \sqrt{\frac{4}{27}}\, \mathrm i \approx 0.4\, \mathrm i\)
Explicit representation and the evaluation
At given \(q\), the cubic equation
\(1+3z^2+4qz^3 = 0\)
has 3 solutions. For positive \(q\), one of these solutions is real and negative, and does not bring new the cut lines of finction ArqNem, as anyway it has cut along the negative part of the real axis. Two other solutions are related with complex conjugation; so, for the evaluation, it is sufficient co consider one of them. Namely this solution is denoted with name NemBra and shown in the parametric plot at right hand side figure as function of \(q\).
Function NemBra can be represented explicitly with combination of radicals, at the appropriate choice of the branch of these radicals.
Let \(~ \rho=-1-8q^2+4\sqrt{q^2+4q^4}\)
Let \(~ V=\rho^{1/3}\)
Then \(~ \displaystyle \mathrm{NemBra}(q)=\frac{1}{4q}\left(-1+V+1/V\right)\)
Extension of power \(1/3\) beyond the cut line and the same about the square root above provides other solutions and other branch points of function ArqNem.
Inverse function
Inverse function of NemBra is denoted with ArcNemBra. In such a way,
\(\mathrm{NemBra}(\mathrm{ArcNemBra}(z))=z\)
ArcNemBra is elementary function,
\(\displaystyle \mathrm{ArcNemBra}(z)= - \frac{1\!+\! 3z^2}{4\, z^3}\)
Complex map of function ArcNemBra is shown in figure at right; \(u\!+\!\mathrm i v=\mathrm{ArcNemBra}(x\!+\!\mathrm i y\). Lines \(u\!=\!\mathrm{const}\) and lines \(u\!=\!\mathrm{const}\) are drawn in the \(x\), \(y\) plane.
Level \(v\!=\!0\) iz marked with pink line. In the First quadrant of the \(x\), \(y\) plane, It is the same line, as the parametric plot of function NemBra for real values of the argument.
Usage
Function NemBra is necessary to determine the cut lines of function ArqNem, in order to choose the appropriate branch for the evaluation.
Function ArqNem is inverse function of the Nemtsov function;
\(\mathrm{Nem}_q(\mathrm{ArqNem}_q(z))=z\)
Function ArqNem is necessary for evaluation of iterates of the Nemtsov function, constructed at zero. These iterates should be used as example of exotic iterates for the book Superfunctions.
It happens, that namely function ArqNem is good for construction of iterates of the Nemtsov Function, while two other its inverse functions ArcNem and ArkNem gives the unnecessary cut lines of the Abel function (denoted as AuNem), and these extra cut lines may reduce the application of the resulting iterates.
References
Keywords
Abel function, ArqNem, AuNem, Exotic iterate, Nemtsov function, Superfunctions