Ru-106
Ru-106 is isotope of Ruthenium.
Atomic mass http://www.periodictable.com/Isotopes/044.105/index.html
105.907329433 amu
Halflife: 373.6 day (decay rate: $2.14736\times 10^{-8}$ Hz )
Primary radioactivity: $1.22 \times 10^{16}$ Bq/Kg
Practical radioactivity: $2.44 \times 10^{16}$ Bq/Kg
Production
Ru-106 is created in the nuclear reactors as product of fission of isotopes of Uranium or Plutonium and seems to be important component of the nuclear waste.
Ru-106 contributes to the relaxation heat of nuclear reactors and the nuclear waste at the scale of order of a year.
Use
$\rm ^{106}_{~44}Ru \xrightarrow[373.6\, day]{\beta^{-},~ .04\, MeV} {} ^{106}_{~45}Rh \xrightarrow[29.8\, s]{\beta^{-},~ 3.54\, MeV} {}^{106}_{~46}Pd $
The intermediate Rh-106 has atomic mass 105.907287135 amu and with halftime 29.8 second converts to stable Pd-106 with atomic mass 105.903485715 amu
Practically, this means, that, at the decay, $\rm ^{106}_{~44}Ru$ produces two beta-electrons and two antineutrinos.
Energies of the two decays can be estimated as follows:
(105.907329433 - 105.907287135) amu c^2/MeV
gives estimate of the energy of the first transition 0.0394 MeV
As for the second transition,
(105.907287135 - 105.903485715) amu c^2/MeV
gives estimate 3.541 MeV
It can be compared to the rest mass of electron, that is estimated to be
0.510998946 MeV
See, for ex., https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_rest_mass
In such a way, the second electron at the cascade decay of Ru-106 seems to have the kinetic energy, roughly, 100 times of the energy of the first one. Perhaps, namely the second electron is detected at the analysis of samples with Ru-106.
The most of energy at each of these two decays seems to be carried out by the antineutrino, and cannot be used.
2017.09.25.Puff
Ru-106 is important contaminant at the nuclear disasters and the barbarian mode of storage, use, recycling of the nuclear waste.
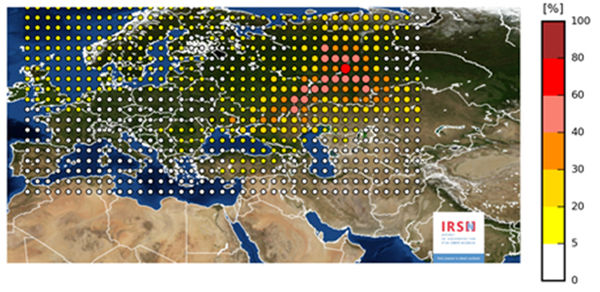
Since 2017.09.25, the huge puff of Ru-106 in Ural (Russia) (or Kazakhstan) is reported by the Western researchers. IRSN estimates that the quantity of ruthenium 106 released was major, between 100 and 300 teraBecquerels, id est, of order of $2\times 10^{14}$Bq, id est, of order of 10 gram of Ru-106.
If an accident of this magnitude had happened in France it would have required the evacuation or sheltering of people in a radius of a few kilometers around the accident site. [4][5][6]
For comparison: amount of unstable isotopes released at the Chernobyl disaster is estimated to be of order of $5\times 10^{18}$Bq, id est, the scale of the 2017.09.25.Puff is 4 orders of magnitude smaller.
The extra Ru-106 is detected over Europe. Then, the location of the source is estimated by numerical analysis of the inverse advection problem.
The Russian and Kazakh administration deny the Ru-106 puff. [7]
Such an observation shows good agreement with the general concept about sabotage of dosimetric groups and Russian administration at the nuclear disasters (they try to kill some part of population rather than confess the grave error or crime). Some examples of such a behaviour of Soviet fascists and evidences in favour of this concept are collected in article Уроки Чернобыля.
The simulated map indicates that the source should be in vicinity of point 55.882, 61.205 ; perhaps, it is just Ozersk (Озёрск).
It looks natural that the Ru-106 is not detected in Russia; the sabotage of dosimetrists and administration in Russia has long tradition since the USSR
(See, Chernobyl disaster),
However, the concept above does not explain, why Ru-106 vaporised at Ozersk is not detected in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Ukraine, Slovakia,
Czekhia, Switzerland, Austria, Hungaria, Italy..
The alternative hypothesis is that few grams of Ru-106 has been dropped into the atmosphere by some aircraft. However, this alternative concept does not explain the appearance to sell localised puff in the simulation of the inverse advection problem.
References
- ↑ http://www.irsn.fr/EN/newsroom/News/Pages/20171109_Detection-of-Ruthenium-106-in-France-and-in-Europe-Results-of-IRSN-investigations.aspx Detection of Ruthenium 106 in France and in Europe: Results of IRSN’s investigations. 09/11/2017.
- ↑ http://www.irsn.fr/EN/newsroom/News/Documents/IRSN_Information-Report_Ruthenium-106-in-europe_20171109.pdf November 9, 2017 of report of 09/10/2017) Detection of ruthenium 106 in France and in Europe Results of IRSN’s investigations. .. Map identifying, on the basis of the model - measurement comparison, the most plausible release zone. For a simulated release at each point of the mesh, the comparison consists in estimating the percentage of modelled data which are within a factor of 2 compared to actual measurements. The area with the highest percentage is identified as the most plausible release zone. .. The exceeding of maximum permitted levels for foodstuffs (1250 Bq/kg for Ruthenium 106 for non - milk products) would be observed over distances of the order of a few tens of kilometres around the location of the release. .. (Last EURATOM Regulation 2016/52 of January 15, 2016 laying down maximum permitted levels of radioactive contamination of food and feed following a nuclear accident or any other case of radiological emergency.)
- ↑ https://www.currenttime.tv/a/28846074.html?nocache=1 Казахстан: мы непричастны к утечке радиации в конце сентября. Карта радиоактивного облака над Европой, составленная Институтом ядерной и радиационной безопасности Франции (IRSN). 2017.11.10.
- ↑ http://www.irsn.fr/EN/newsroom/News/Pages/20171004-Detection-ruthenium-106-in-the-air-in-Europe.aspx Detection of ruthenium 106 in the air in the east and south-east parts of Europe. 04/10/2017. Ruthenium 106 has been detected by several European networks involved in the monitoring of atmospheric radioactive contamination. Ruthenium 106 is a radionuclide of artificial origin. It is a fission product from the nuclear industry. This radionuclide is also used in the medical field for brachytherapy treatments. The Austrian Ministry of the Environment published Tuesday October 3rd 2017 a statement indicating that it detected small quantities of ruthenium without consequences for environment and health. The Norwegian Nuclear Safety Authority (NRPA) issued a press release also reporting low levels of ruthenium in the atmosphere. For its part, the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) gave its first results of measurements indicating "low levels of radioactivity in the air". These measurements "revealed traces of ruthenium-106, a radioactive element with a half-life of 373.6 days, in aerosols taken from Cadenazzo, Ticino, between 25 September and 2 October 2017. The concentration of ruthenium 106 amounts to about 40 micro-Bq / m3, which is 17 000 times lower than the limit of air emissions set for this radionuclide in the Radiation Protection Ordinance."// Since October 3, 2017, IRSN has mobilized all its measurement stations for atmospheric monitoring and undertook the analysis of their filter samples...
- ↑ https://af.reuters.com/article/worldNews/idAFKBN1D92MN Geert De Clercq. French institute suspects nuclear accident in Russia or Kazakhstan in September. November 9, 2017 / 5:53 PM. PARIS (Reuters) - A cloud of radioactive pollution over Europe in recent weeks indicates that an accident has happened in a nuclear facility in Russia or Kazakhstan in the last week of September, French nuclear safety institute IRSN said on Thursday. .. This could indicate Russia or possibly Kazakhstan, an IRSN official said. .. IRSN estimates that the quantity of ruthenium 106 released was major, between 100 and 300 teraBecquerels, and that if an accident of this magnitude had happened in France it would have required the evacuation or sheltering of people in a radius of a few kilometers around the accident site.
- ↑ 2017.10.09. http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/technik/radioaktives-ruthenium-106-quelle-vermutlich-im-suedlichen-ural-a-1171859.html In Deutschland gemessenes Ruthenium soll aus dem Ural stammen Das radioaktive Element Ruthenium-106 wurde in den vergangenen Tagen in Deutschland, Italien und Österreich nachgewiesen. Experten vermuten die Quelle in Russland. Montag, 09.10.2017 10:33 Uhr. In Deutschland gemessenes Ruthenium soll aus dem Ural stammen Das radioaktive Element Ruthenium-106 wurde in den vergangenen Tagen in Deutschland, Italien und Österreich nachgewiesen. Experten vermuten die Quelle in Russland. // Seit etwa einer Woche werden an mehreren Messstellen in Europa leicht erhöhte Werte von Ruthenium in der Luft nachgewiesen. Unter anderem an Stationen des Deutschen Wetterdienstes sowie auch an mehreren europäischen Stationen, etwa in Österreich und Italien. Nach Berechnungen von Experten wurde das radioaktive Material in der letzten Septemberwoche freigesetzt. // Die nun in Europa gemessene Konzentration ist jedoch sehr gering. So betrage die höchste in Deutschland gemessene Konzentration von Ruthenium in Görlitz etwa 5 Millibecquerel pro Kubikmeter Luft. ..
- ↑ http://www.infotekst.ru/zhaloby/radiaciya-proshla-mimo-rossiyan-i-kazakho.html george. Радиация прошла мимо россиян и казахов, но заинтересовала французов. Ноя 10, 2017. .. По мнению специалистов этого авторитетного исследовательского центра, в конце сентября этого года в районе, предположительно, между южным Уралом и Волгой, произошел мощный выброс рутения 106, не встречающегося в естественных условиях в природе. .. Между тем, российские власти заявили, что не знают об аварии на их территории, — заявил агентству Рейтер директор IRSN Жан-Марк Перес, — и добавил, что институт еще не контактировал с властями Казахстана. .. Что же касается пораженных территорий Казахстана или России, то здесь слова за местными специалистами, которые молчат или говорят, что ничего не происходило.
http://www.periodictable.com/Isotopes/044.106/index.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_decay
http://www.twirpx.com/file/437859/ Казенас Е.К., Чижиков Д.М. Давление и состав пара над окислами химических элементов. 28.03.11 02:31.
Keywords
2017.09.25.Puff, Advection, Bigpuf, Corruption, Designate Russia as state sponsor of terrorism, Nuclear disaster, Pahanat, Puff, Ru-106 , Russia, Sabotage